What is a two-stage compression refrigeration cycle?
Two stage compression refrigeration cycle means that the refrigerant vapor from the evaporator is compressed twice by the low-pressure and high-pressure compressor before entering the condenser. An intercooler shall be set between the two compressions.
The two-stage compression refrigeration cycle system can be a double machine composed of two compressors.
(one is a low-pressure compressor and the other is a high-pressure compressor) the two-stage system can also be a single-stage two-stage system composed of one compressor, in which one or two cylinders are used as high-pressure cylinders and the other cylinders are used as low-pressure cylinders. The number ratio of high and low-pressure cylinders is generally 1:3 or 1:2.
Refrigeration cycle process of two-stage compression system
The high-pressure liquid from the high-pressure liquid storage tank is divided into three routes:
All the way to the main regulating station to supply the system with higher temperature.
The other is sent to the intermediate cooling tower after throttling and expansion to cool the superheated ammonia steam discharged from the low-pressure stage and the high-pressure liquid in the discharge pipe.
Finally, the serpentine exhaust pipe entering the intermediate cooling tower is throttled after being cooled in the intermediate cooling tower and supplied to the system with low evaporation temperature. The ammonia oil separator is to reduce the pollution of lubricating oil to the serpentine row pipe in the intermediate cooling tower, so as to keep the heat transfer coefficient of the serpentine row pipe in a normal state.
Classification of two-stage compression refrigeration cycle
According to the intermediate cooling mode, the two-stage compression refrigeration cycle can be divided into intermediate complete cooling cycle and intermediate incomplete cooling cycle;
The intermediate cooling mode of two-stage compression refrigeration cycle is related to the type of refrigerant. For example, in the ammonia two-stage refrigeration compressor, the intermediate complete cooling cycle is generally adopted; In the Freon two-stage refrigeration compressor, the intermediate incomplete cooling cycle is mostly used. This is because the adiabatic index of freon refrigerant is smaller than that of ammonia and has little effect on the exhaust temperature.
According to the throttling mode, the two-stage compression refrigeration cycle can be divided into one-stage throttling cycle and two-stage throttling cycle. The so-called intermediate complete cooling refers to cooling the exhaust of the low-pressure stage to the saturated steam under the intermediate pressure.
If the low-pressure stage exhaust is cooled but not cooled to saturated steam, it is called intermediate incomplete cooling. If the high-pressure liquid is throttled from the condensation pressure PK to the intermediate pressure PM, and then throttled and depressurized from PM to the evaporation pressure Po, it is called a two-stage throttling cycle. If the refrigerant liquid is directly throttled from the condensation pressure PK to the evaporation pressure Po, it is called a primary throttling cycle.
The dynamic diagram of two-stage compression refrigeration cycle is as follows:
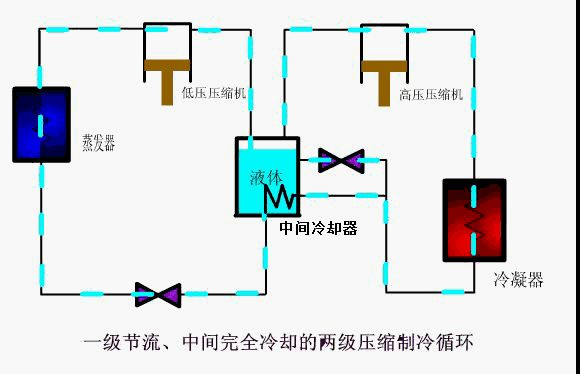
① A two-stage compression refrigeration cycle with one-stage throttling and complete cooling in the middle
Schematic diagram of refrigeration cycle
working process
The low-pressure and low-temperature refrigerant vapor generated in the evaporator is sucked by the low-pressure compressor and compressed into superheated vapor with intermediate pressure, and then enters the intercooler with the same pressure and is cooled into dry saturated vapor in the intercooler. The medium pressure dry saturated steam is sucked by the high-pressure compressor and compressed to the superheated steam at the condensation pressure, and then enters the condenser to be condensed into refrigerant liquid. Then it is divided into two ways. One way enters the intercooler after throttling and pressure reduction through expansion valve f, and most of the liquid enters the coil of the intercooler for subcooling from the other way. However, due to the heat transfer temperature difference, it cannot be cooled to the intermediate temperature in the coil, but it is generally higher than the intermediate temperature △ t = 3-5 ℃. The supercooled liquid is throttled and depressurized into low-temperature and low-pressure supercooled liquid through the main expansion valve, and finally enters the evaporator for heat absorption and evaporation to produce cooling effect.
This cycle system is only applicable to the two-stage refrigeration cycle system of R717 and R22.
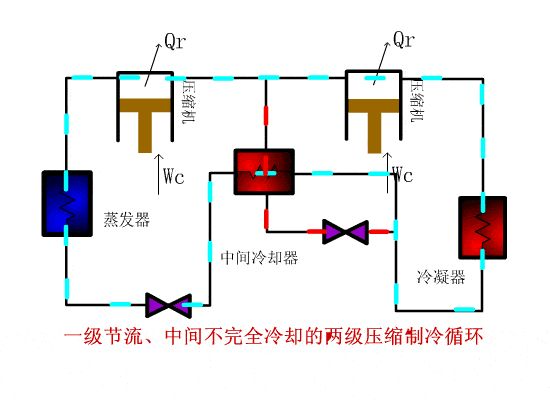
② A two - stage compression refrigeration cycle with one - stage throttling and incomplete cooling in the middle
Refrigeration cycle intention
Working process:
After passing through the regenerator, the steam from the evaporator is sucked into the low-pressure compressor, compressed to the intermediate pressure and mixed with the dry saturated steam from the intercooler in the pipeline, so that the superheated steam discharged from the low-pressure machine is cooled and then enters the high-pressure compressor, compressed to the condensing pressure and enters the condenser. The condensed high-pressure refrigerant liquid enters the serpentine coil of the intercooler for re cooling, then enters the regenerator for heat exchange with the low-temperature and low-pressure steam from the evaporator to cool the supercooled liquid from the serpentine coil of the intercooler again, and finally enters the evaporator through the expansion valve for heat absorption and evaporation.
This cycle system is only applicable to the two-stage refrigeration cycle system of R717 and R22.
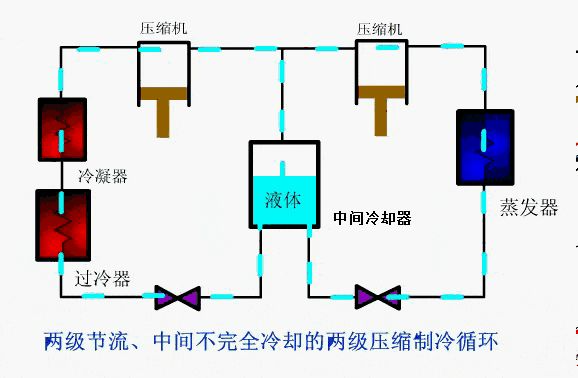
③ Two stage compression refrigeration cycle with two-stage throttling and complete cooling in the middle
Refrigeration cycle intention
working process
The saturated vapor of the refrigerant from the evaporator is sucked in by the low-pressure stage compressor and compressed to the intermediate pressure PM, and then discharged into the intercooler. It is cooled by the refrigerant liquid in it into saturated vapor. At the same time, part of the liquid refrigerant in the intercooler absorbs heat and becomes saturated vapor. They enter the high-pressure stage of the compressor together and are compressed to the condensation pressure PK again. It enters the condenser and condenses into saturated liquid, depressurizes to the intermediate pressure PM through throttle valve a, and enters the intercooler to separate into steam and liquid. In the intercooler, a small part of the liquid refrigerant is used to cool the exhaust of the low-pressure stage into steam, and is sucked back by the high-pressure stage together with the steam generated by the low-pressure exhaust and throttling. Most of the liquid refrigerant is throttled to the evaporation pressure P0 through throttle valve B and enters the evaporator to produce cooling capacity. The cycle is carried out again and again.
This type of refrigeration cycle system is only applicable to the two-stage compression refrigeration cycle system of R717 or R22. In order to prevent the saturated liquid from the intercooler from flashing into steam in the pipeline, the distance between the intercooler and the evaporator is usually required to be close.
④ Two stage compression refrigeration cycle with two-stage throttling and incomplete cooling in the middle
This cycle is suitable for Freon centrifugal refrigerator.
⑤ A two-stage compression refrigeration cycle with two-stage throttling and complete cooling in the middle with an intermediate evaporator.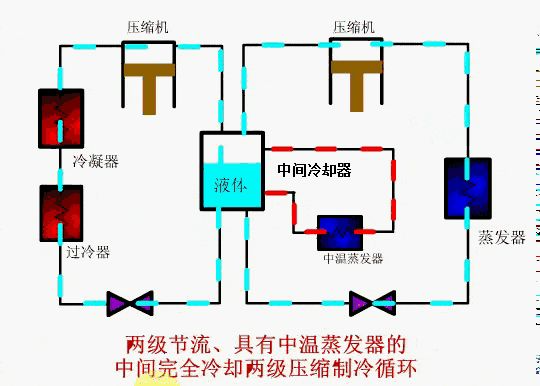
LATEST NEWS
- What is the difference between refrigerator refrigeration single cycle, double cycle and three cycle? How to distinguish? 2021-12-06 15:33:40
- What is a two-stage compression refrigeration cycle? 2021-12-06 15:32:32
- Why did semiconductor refrigeration not replace compressor refrigeration? 2021-12-02 13:57:29
- Explanation of working principle of refrigeration equipment of refrigeration unit 2021-12-02 13:50:37
- Details needing attention in improving reaction rate of industrial high and low temperature circulating device 2021-12-02 13:48:26
- What is the role of China's breakthrough in ultra-low temperature refrigeration technology, which is 0.01 degrees different from absolute zero? 2021-12-02 13:43:08



Nicole Wu
Email: sale5@pro -valves.com
MOBILE: +86 13968609917